This guide walks you through what is required on your React Native app in order to perform a SubscriberCheck using tru.ID's (IDlayr) React Native SDK. However, if you wish to see the finished working example app, you can find it on our GitHub respository. It covers:
- What you need before you begin implementation
- Install tru.ID (IDlayr) React Native SDK
- How to implement into my app?
- Set up and run the React Native example application
- Performing a SubscriberCheck on React Native
1. Before You Begin
To fully understand the functionality required to create a SubscriberCheck in this guide, you will need to carry out some initial steps, such as creating an account, a project, and retrieving your workspace credentials. You'll also need to have an understanding of the workflow for a SubscriberCheck to be successfully carried out.
The first step is to Setup Your Environment. This page walks you through what parts are required, such as installing the IDlayr CLI, creating a project, and if needed, running the demo development server.
The second step is to gain more of an understanding of how the SubscriberCheck works. The Integration Guide provides a step by step guide on the workflow of a SubscriberCheck, and which devices need to act at what points of the workflow.
2. Install tru.ID (IDlayr) React Native SDK
The tru.ID (IDlayr) React Native SDK on Android requires a minimum API level of 21 (Android 5), and a compile level needs to be API 30 (Android 11) or later.
The Flutter SDK on iOS requires a minimum iOS 12+.
In the project's Android directory, open the build.gradle file, add the tru.ID's (IDlayr) Android SDK public repository within the buildscript and allprojects repository sections, similar to what's shown below:
buildscript {repositories {...maven {url "https://gitlab.com/api/v4/projects/22035475/packages/maven"}}...}allprojects {repositories {...maven {url "https://gitlab.com/api/v4/projects/22035475/packages/maven"}}}
Then in your terminal, within the project's root directory run the following command to install the React Native SDK as a dependency:
npm install @tru_id/tru-sdk-react-native
3. How to implement into my app?
Importing and Initializing the SDK
Before proceeding, be sure to sync your project for these new dependencies to be installed.
Initialize tru.ID (IDlayr) SDK
import TruSdkReactNative from "@tru_id/tru-sdk-react-native";
Reachability
The Reachability API is a feature that enables applications to check whether the SIM card within a user's device is on a network that IDlayr has connectivity to.
The React Native SDK has functionality built in to call the reachability, to call this you would need to run the following code:
const details = await TruSdkReactNative.isReachable();
If the mobile network operator is supported by IDlayr then a JSON object is returned similar to the example below:
{"network_id": "23410","network_name": "O2 UK","country_code": "GB","products": [{"product_id": "SCK","product_name": "SubscriberCheck"}]}
However, if it isn't supported, then an error is returned in JSON format.
Call your backend server to create SubscriberCheck
As described in the Integration guide step 1 is to create a SubscriberCheck. This step is a step where your mobile application needs to call your backend server with the mobile devices telephone number. Your backend server then makes a POST request to IDlayr's SubscriberCheck API. If successful, the SubscriberCheck API will return a response with the check_id and a unique check_url. Your backend server needs to return this check_url to the mobile device.
Open Check URL to process SubscriberCheck
Step 2 of the integration guide is to process the SubscriberCheck. This step is a step where the mobile application makes a GET request to the check_url provided in the previous step. The mobile device application then needs to follow all redirects, then on the last redirect, the JSON response will contain a code. This code will be used next.
await TruSdkReactNative.checkUrlWithResponseBody(url);
Call Backend server to complete SubscriberCheck
Step 3 of the integration guide is to complete the SubscriberCheck. This step is a step where the mobile application makes a POST request to your backend server with the check_id and the code. Your backend server then makes a PATCH request to /subscriber_check/v0.2/checks/{check_id} with the JSON body below to complete the SubscriberCheck process:
[{"op": "add","path": "/code","value": "{check_code}"}]
Within the response of this PATCH request, there will be a field
no_sim_change, this is the field used to show if the SIM card has been
changed recently, which could be an indication whether the owner of the SIM
card may be a victim of SIM swap fraud. If the value is true, then proceed
with the SubscriberCheck.
Finally, your backend server would need to return a success or failure response to your mobile application to allow the user of this application to proceed.
4. Setup the React Native example application
Clone and configure the React Native example application
Open a new terminal and ensure you are in the tru-id-phonecheck-example working directory. Run the following command to clone the React Native example into a app-example-react-native directory:
git clone [email protected]:tru-ID/app-example-react-native.git
And navigate into the newly created app-example-react-native directory:
cd app-example-react-native
Install the application dependencies:
yarn install # or npm install
Create a copy of the .env.example file, naming the new file .env:
cp .env.example .env
And update the configuration value for BASE_URL in .env to point to the public ngrok URL of the Node.js example server. For example:
BASE_URL=https://d88e00a17e1c.ngrok.io
Install and run the React App on Android
Detailed information on running an application on a device can be found in the
React Native documentation
.
Ensure your Android device is connected to your computer via USB with developer mode and USB debugging enabled.
Run the following in the terminal:
yarn android # or npm run android
The terminal output will look similar to the following:
react-native run-androidinfo Running jetifier to migrate libraries to AndroidX. You can disable it using "--no-jetifier" flag.Jetifier found 968 file(s) to forward-jetify. Using 8 workers...info JS server already running.info Installing the app...Downloading https://services.gradle.org/distributions/gradle-6.8-bin.zip..........10%..........20%..........30%...........40%..........50%..........60%..........70%...........80%..........90%..........100%<===----------> 27% EXECUTING [25s]BUILD SUCCESSFUL in 1m 57s48 actionable tasks: 48 executedinfo Connecting to the development server...info Starting the app on "08231FDD4004V7"...Starting: Intent { cmp=com.example.trusdkreactnative/.MainActivity }✨ Done in 119.80s.
This will run a Metro server in a new terminal tab or window and install the React Native application to your USB connected Android application.
Install and run the React App on iOS (MacOS only)
Detailed information on running an application on a device can be found in the
React Native documentation
.
Run the Metro development server:
yarn start # or npm start
Install the project dependencies:
cd ios && pod install
Ensure your iOS device is connected via USB. Open up ios/TruSdkReactNativeExample.xcworkspace in XCode and set your iOS device as your deployment target:
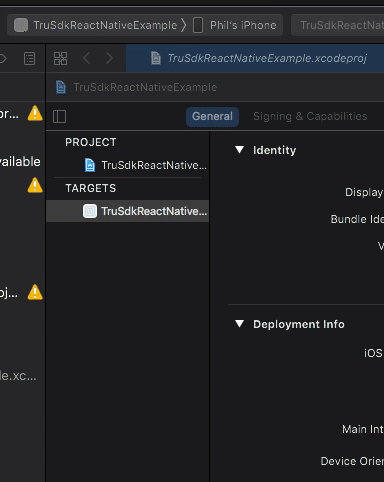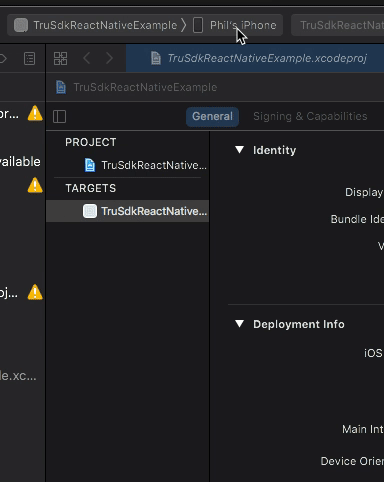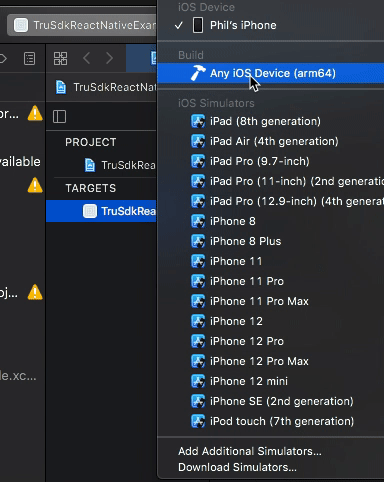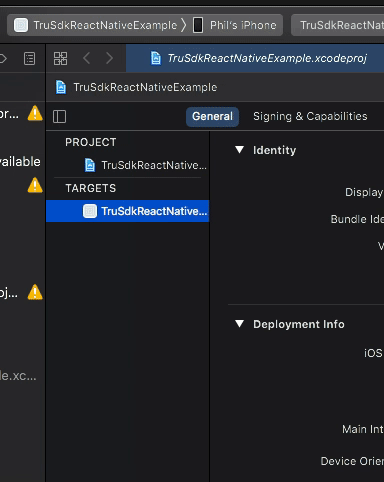
Finally, select "Run" in XCode to install and run the application on your iOS device.
5. Perform a SubscriberCheck
Enter your phone number including the country code and click "Verify my phone number". The application will look similar to the following:
With that, you've completed your first SubscriberCheck from a React Native application.
6. Resources
- SubscriberCheck full integration guide
- Node.js server application on GitHub
- React Native example application on GitHub
- tru.ID (IDlayr) SDK for React Native on GitHub
- SubscriberCheck API Reference
7. Troubleshooting
Error: Could not find or load main class org.gradle.wrapper.GradleWrapperMain when running yarn android
The gradle wrapper is missing, broken or corrupted.
Ensure Gradle is installed and fex the gradle wrapper by running the following in the terminal from the android directory:
gradle wrapper
For more information see this Stack Overflow answer.


